
Character cartoon
Introduction to Character Cartoon in Animation
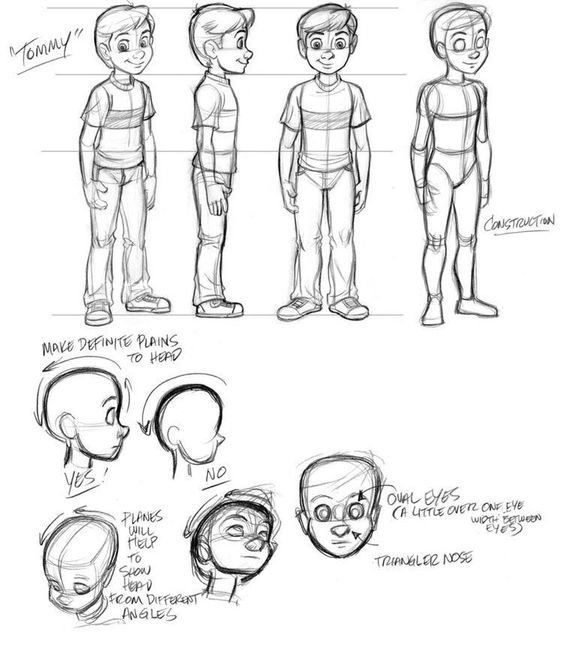
Character cartoon are the foundation of the animation business. In order to appeal to a wide audience, stylized, exaggerated, and frequently hilarious characters are created. These characters are essential to narrating a story in an animated media and can be anything from humans to animals, legendary creatures to inanimate objects.
Defination of cartoon character
A character cartoon is an animated stylized depiction of a person, animal, or object. Cartoon characters, as opposed to realistic depictions, frequently have exaggerated features, such as big eyes, enormous heads, or exaggerated expressions, which make personality traits and emotions more clearly conveyed. Characters created in this manner are more captivating and memorable due to the abundance of creative options available.
design character
A cartoon character’s character design is a crucial component. Determining the character’s physical attributes, disposition, and conduct is necessary. To make sure the character fits the plot and the setting, the design process involves drawing, modeling, and fine-tuning the character.
Visual Appeal
The cartoon character’s aesthetic appeal is quite important. Designers create visually striking characters that instantly convey a character’s personality and role using color schemes, forms, and proportions. For instance, artists often use circular forms to represent amiable or humorous characters, while they use sharp angles to depict villains.
Personality and Traits
Giving the character particular personality qualities is another aspect of character creation. The way the character looks and moves frequently reflects these qualities. A heroic figure might, for example, have a powerful, straight stance, whereas a cunning one might have a sly smile and rapid, darting motions.
Role of Exaggeration in Cartoons
A key element in the creation of cartoon characters is exaggeration. Animators can increase a character’s expressiveness and add entertainment value to their activities by exaggerating specific traits or mannerisms.
Physical Exaggeration
Exaggerated gestures and huge heads and eyes are examples of physical exaggeration. By emphasizing the character’s feelings and behaviors, this strategy helps the viewer find the character more sympathetic and enjoyable. When a character is shocked, for instance, their eyes may enlarge far more than they would in real life.
Emotional Exaggeration
The purpose of emotional exaggeration is to highlight a character’s emotions and responses. This can include exaggerated displays of joy, sorrow, fear, or rage. To make a figure more alive and captivating, animators can intensify these feelings to their utmost.
Types of Cartoon Characters
Cartoon characters come in a variety of forms, and they all have distinct functions within a narrative. Comprehending these categories facilitates the efficient development and application of characters in animation.
Protagonists
Protagonists, who are central to the narrative, have distinct objectives and motives. The story often presents them as likable and approachable. Throughout the narrative, the audience should be able to relate to the character due to their unique design and demeanor.
Antagonists
Antagonists oppose the protagonist, often appearing with darker hues or more angular shapes to convey an ominous or frightening aesthetic. The antagonist’s job is to fuel conflict so that the story can move on.
Sidekicks
Supporting characters known as sidekicks frequently offer comic relief or help to the main character. Typically, they are made to be charming or funny, with peculiar qualities that go well with the main character.
Background Characters
The animation’s setting includes background characters that add depth and realism. Their design adds to the overall mood and feel of the story even though they are not essential to the plot.
Animation Techniques for Character Cartoons
Cartoon creatures come to life thanks in large part to animation techniques. These methods define a character’s movements, emotional expressions, and interactions with their surroundings.
Traditional Animation
Every frame of a traditional animation is manually drawn. This method gives you a great deal of control over the actions and facial emotions of the character. Although it takes a lot of work, it gives the animation a distinctive, organic feel.
Digital Animation
Digital animation, including 2D and 3D animation, uses software to design and animate creatures. This approach proves more effective, allowing for intricate effects and fluid movements. Additionally, digital tools provide greater flexibility for editing and refining character animations.
Stop Motion
In stop motion, animators physically alter characters and capture each change on camera frame by frame. They frequently apply this technique to characters made of clay or other materials, which gives the animation a distinctive, tactile feel.
Conclusion
In animation, character cartoons go beyond simple illustrations; artists skillfully create them as works of art intended to captivate, amuse, and tell a tale. They design character cartoons painstakingly at every stage, from the original concept to the finished animation, ensuring that viewers find them engaging. These characters, whether they serve as the antagonist, the hero, or the comedic relief, are undeniably essential to the animation industry. Firstly, they bring tales to life through their dynamic roles. Moreover, their presence has a profound effect on audiences of all ages, thereby enhancing the overall impact of animated stories. Consequently, they play a crucial role in the success and appeal of animated content.
What is a 3D Cartoon Character?
A 3D cartoon character is a digital figure created using three-dimensional (3D) modeling techniques. Unlike traditional 2D cartoons that are flat and drawn on a single plane, 3D characters have depth, allowing them to appear more lifelike and realistic. Here’s a simple breakdown of what makes up a 3D cartoon character:
1. 3D Modeling
Definition: 3D modeling is the process of creating a three-dimensional representation of a character using specialized software.
Techniques: Artists use software like Blender, Maya, or 3ds Max to sculpt the character’s shape. This involves building a mesh or wireframe that defines the character’s structure.
Details: The model is then refined with details such as facial features, clothing, and accessories.
2. Texturing
Definition: Texturing involves applying colors, patterns, and materials to the 3D model to give it a realistic appearance.
Materials: Textures can include skin tone, clothing patterns, and surface textures like fur or metal.
Process: Artists paint textures directly onto the 3D model or use photographs to create realistic surfaces.
3. Rigging
Definition: Rigging is the process of creating a skeleton or framework for the character so it can move.
Bones: This “skeleton” includes bones and joints that allow the character to bend and pose.
Controls: Rigging also involves setting up controls for animators to manipulate the character’s movements.
4. Animation
Definition: Animation is the process of bringing the 3D character to life by creating movements and actions.
Techniques: Animators use keyframes to define specific poses or expressions and then fill in the motion between these keyframes.
Effects: The character’s movements can be further enhanced with special effects like running, jumping, or facial expressions.
5. Rendering
Definition: Rendering is the final step where the 3D character is transformed into a 2D image or animation sequence.
Process: This involves calculating light, shadows, and textures to produce the final visual output.
Quality: The quality of rendering can affect how realistic or stylized the character appears.
6. Application
Usage: 3D cartoon characters are used in various media, including movies, video games, TV shows, and virtual reality experiences.
Purpose: They provide engaging and interactive experiences by combining visual appeal with dynamic movement and expression.
By combining these elements, 3D cartoon characters offer a rich, interactive experience that can be both visually stunning and highly engaging.












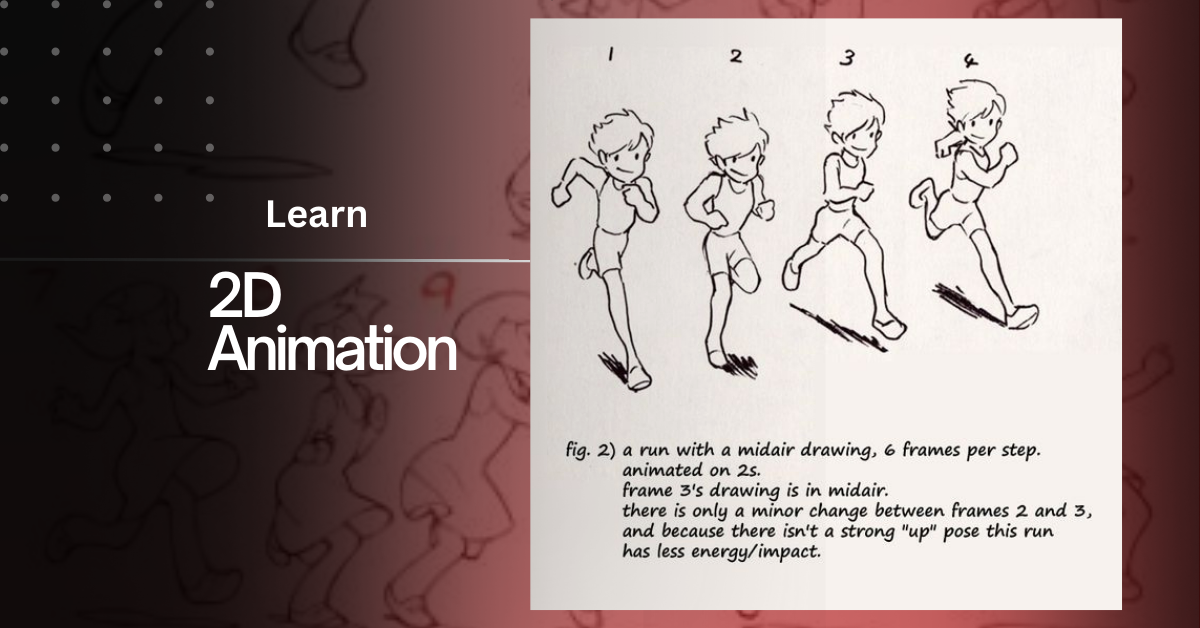
Leave a Reply